Guide to understanding technical data sheets for extruded aluminum profiles
What are aluminum extrusion profile specifications and why they matter
When you’re working with aluminum extrusion profiles, it’s important to know that the specifications aren’t just a bunch of numbers—they tell you everything about how that profile will perform in real life. These details cover the physical, mechanical, and chemical properties, and they’re the backbone for making sure your extruded aluminum components will work the way you need them to, whether it’s for a building facade, aluminum panels, or any other project.
In a nutshell, these specs help architects, contractors, and project managers compare different options, check if they meet the right standards, and make smart choices. If you pick a profile with the wrong tolerance or an unsuitable alloy, you might end up with pieces that don’t fit right, or worse, a system that doesn’t hold up over time. That’s why technical data sheets are so valuable—they help you match the right product to your project and set you up for long-term success.
Something you should keep in mind is that these specifications go beyond just making sure things fit together. They also determine if the profile can handle things like wind, changes in temperature, or exposure to moisture and pollution. Especially in public or commercial buildings, following standards from groups like ASTM International or the American Architectural Manufacturers Association isn’t just a suggestion—it’s usually required. These standards lay out the minimums for things like strength and corrosion resistance, and you’ll want to double-check these details in the datasheet before you move forward. Plus, following these specs can make the whole process smoother, from fabrication and assembly to maintenance, which can save you time and money down the line.
How to read aluminum extrusion datasheets step by step
If you’ve ever looked at an aluminum extrusion datasheet and felt overwhelmed, don’t worry—you’re not alone. The key is to break it down step by step:
Start by looking at the profile type and cross-sectional geometry. This tells you what shape you’re dealing with and helps you figure out if it’s right for your project, like for aluminum battens or metal cladding.
Check out the alloy series and temper. These details affect how strong the profile is, how well it resists corrosion, and how easy it is to work with.
Make sure the listed dimensions and tolerances will work with your aluminum systems and any other parts you’re using.
Consider whether the product meets industry standards—look for references to the American Architectural Manufacturers Association or ASTM International in the datasheet.
Review the surface finish and coating options. These choices can make a big difference in how your project looks and how well it stands up to the elements.
Pay attention to things like weight per unit length and load-bearing capacity, especially if you’re doing structural calculations.
Some datasheets go a step further and include tips on fabrication—like whether you can cut, drill, or weld the profile easily. You might also see info about environmental certifications, which matters if you’re aiming for green building credentials like LEED. It’s always a good idea to double-check that the manufacturer’s documentation matches your project specs and local building codes. For instance, a 6063-T5 profile might be perfect for curtain wall framing, while a 6061-T6 profile could be better for structural supports. Real-world comparisons like these help you see how the numbers translate into actual performance.
Key sections found in technical datasheets
Every technical datasheet for extruded aluminum profiles has some must-have sections:
Profile description: Usually comes with a technical drawing or cross-section, so you can visualize the shape.
Dimensions and tolerances: Spell out exactly how much the width, height, wall thickness, and other measurements can vary.
Alloy and temper: Details like 6063-T5 or 6061-T6 let you know what kind of mechanical properties to expect.
Mechanical properties: Includes numbers for tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation—important for structural analyses.
Surface finish: Tells you if the profile comes anodized, powder-coated, or with a mill finish.
Additional info: Sometimes includes corrosion resistance, regulatory compliance, or even recommended uses.
Other possible sections:
Thermal or electrical conductivity (for specialized settings)
Fire resistance ratings or certifications (for architectural projects)
Maximum span or recommended fasteners (for easier installation)
List of compatible accessories, like brackets or gaskets
References to third-party test reports or certifications (for unique or large projects)
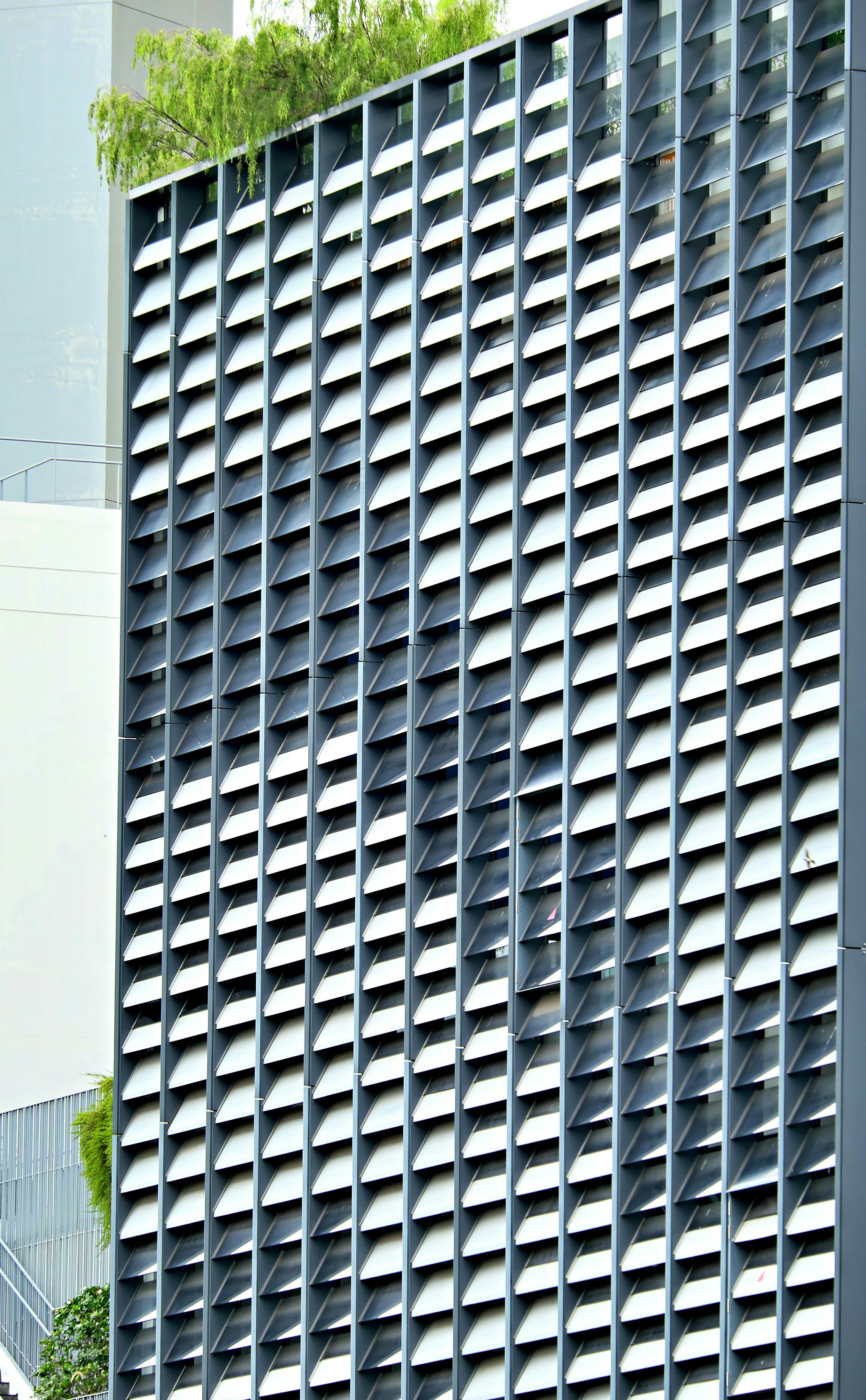
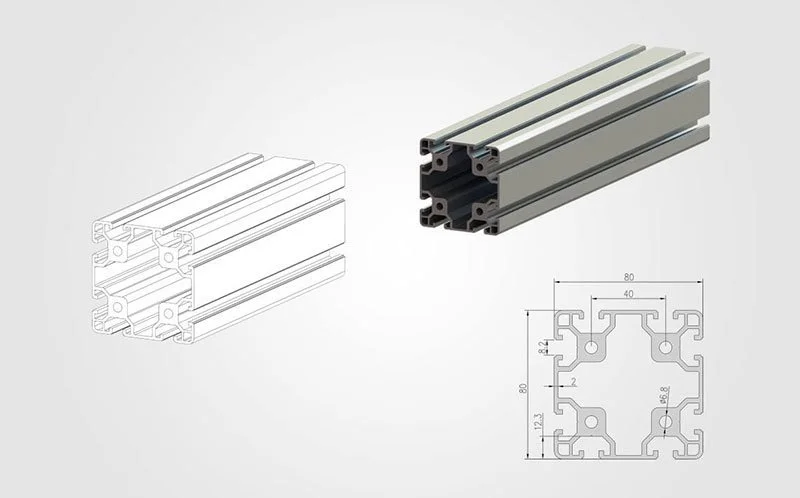
Understanding aluminium extrusion dimensions and profile geometry
When we talk about aluminum extrusion specifications, dimensions and geometry are at the heart of it.
Dimensions: Width, height, depth, wall thickness, and length. Getting these numbers right is key if you want the profile to fit seamlessly into your aluminum systems, whether it’s window frames, curtain walls, or aluminum panels.
Profile geometry: All about the cross-sectional shape, which directly affects both strength and appearance. Profiles may have internal channels, flanges, or reinforcement ribs for specific purposes.
For example, if you’re working on a building facade, you might need a custom shape to connect with other exterior cladding elements or to fit a particular installation method.
It’s important to know that even small mistakes in reading these dimensions can lead to big problems, like misalignment or weak spots that jeopardize the entire facade. Some projects call for profiles that are modular or compatible with standardized systems. For example, if you’re installing aluminum panels in a rainscreen cladding system, the profiles need to work smoothly with waterproof membranes or insulation. Geometry can also play a role in energy efficiency, since thicker walls or extra chambers can help with insulation and reduce unwanted heat transfer. It’s always smart to compare the datasheet’s dimensions with shop drawings or BIM models before you start building. Many manufacturers now offer 3D CAD files or detailed technical drawings to make this process easier.
Aluminum profile tolerances and their impact on facade performance
Let’s talk about tolerances—a detail that’s easy to overlook but makes a huge difference.
Tolerances tell you how much a profile’s dimensions can vary from the stated values.
They’re essential for getting a proper fit and smooth alignment, especially when you’re piecing together systems like aluminum cladding, aluminum siding, or exterior cladding.
If the tolerances are too loose, you could end up with installation headaches or even structural issues.
For facade projects, tolerances don’t just affect how things look—they also play a big role in weather resistance and how the system handles weight and stress. If profiles don’t meet the specified tolerances, you might see gaps, water leaks, or heat loss, all of which can shorten the life of your building envelope. So, it’s a good idea to select profiles with tolerances that match the requirements in the technical datasheet. This step is key to making sure your aluminum panels or building facade will perform as expected for years to come.
Out in the field, the consequences of missing the mark on tolerances can be expensive. Imagine a curtain wall system where the profiles are just a bit off—you could face air or water leaks and end up with costly fixes. Groups like the American Architectural Manufacturers Association set minimum requirements for things like air and water tightness, and hitting those targets depends on having precise profiles. It’s always smart to measure and check everything during installation, and for big projects, running a mock-up first can help you spot any issues before they become a real problem.
Tolerances in architectural aluminum extrusions
When it comes to architectural aluminum extrusions, tolerances are usually set by organizations like ASTM International or the American Architectural Manufacturers Association. These standards spell out what’s acceptable for measurements like width, height, straightness, twist, and flatness.
For example, you might see a wall thickness tolerance of ±0.15 mm, but that can change based on the profile’s size and use.
Manufacturers will typically list these tolerances in the datasheet and reference the standard they follow.
It’s important to double-check these numbers, especially if the profiles will be visible or need to fit tightly with things like aluminum battens or metal cladding.
For high-profile or custom projects, you might need even stricter tolerances to make sure everything lines up perfectly.
Standards such as ASTM B221 and AAMA 611 go into great detail about what’s allowed for different types of extruded aluminum. They offer tables and formulas to help you figure out if a profile meets the mark. If you’re working on something unique, your project specs might call for even tighter tolerances than usual, especially if you’re aiming for a flawless finish. When reviewing datasheets, don’t hesitate to ask the manufacturer for certificates of compliance or quality reports if you need that extra assurance.
Alloys and design considerations for architectural aluminum profiles
Choosing the right alloy is a big deal when you’re working with aluminum extrusion profiles.
The 6000-series alloys are popular because they strike a good balance between strength, workability, and corrosion resistance, making them a solid choice for things like aluminum panels or aluminum siding.
Every alloy has its own set of strengths, and picking the right one can make a big difference depending on your environment and performance needs.
There’s more to consider, too:
Which surface treatments work best
What kind of joining methods you’ll use
Whether the profile will play nicely with other building materials
Some alloys are better for anodizing or powder coating, which can keep your project looking great and help it last longer. At the end of the day, the alloy you choose needs to meet both the structural and visual goals for your aluminum systems or building facade.
For example:
6063 is known for its smooth finish, so it’s great for visible parts of a facade.
6061 is stronger and often used for framing or load-bearing sections.
If your project is near the coast or in an industrial area, you might need an alloy or coating that stands up to salt or pollution.
Don’t forget about how the profile will be assembled—will it need to hold fasteners or sealants?
If you’re working with curtain wall systems, profiles might include built-in thermal breaks or drainage channels, which means the alloy and design have to work hand in hand.
Aluminum extrusion design in facade applications
Designing extruded aluminum profiles for facades is a bit of an art and a science.
The geometry needs to handle the loads and make room for connections with other facade elements, like panels, battens, or structural supports.
Paying close attention in the design phase helps you avoid headaches during installation and keeps everything running smoothly.
You’ll also need to keep an eye on building codes and standards, since these can dictate things like fire resistance, wind load, and thermal performance. Choosing profiles with the right finishes and coatings is a smart way to boost weather resistance and keep your building looking sharp for years. If you take the time to think through design, alloy selection, and tolerances, you set yourself up for a facade that’s not just durable, but also visually consistent and high-performing.
It’s worth noting that a successful facade often comes from teamwork—architects, engineers, and manufacturers working together to get every detail right. For instance, using aluminum battens with hidden fasteners can give you a sleek look without making installation harder. In taller buildings, you might need reinforced profiles to handle higher wind loads. Local energy codes could require thermally improved profiles or insulated panels, especially if you’re aiming for energy efficiency. Mock-ups and performance tests, like checking for water leaks or structural strength, are common steps before going all-in on a big project. By making the most of the technical data in aluminum extrusion datasheets and sticking to best practices, you can reach both the practical and design goals for today’s facade systems.